The Treebolic architecture is modular.
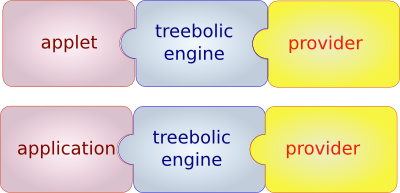
Components
The Treebolic or core is a component (or widget) that delivers a hyperbolic representation of a hierarchical set of data organized as a tree.
The application (either a basic application or applet or browser or generator or plugin or ...) hosts the Treebolic. Communication between application and engine works both ways.
The provider is responsible for feeding data to the Treebolic. Communication between provider and engine also works both ways.
Providers
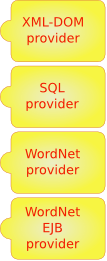
Generic providers - N-Tier providers
Some providers can be factored out in generic providers (xslt/graph) that interact with a specific part.
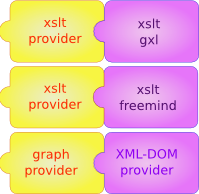
- The XSLT generic provider lays the basis for derived classes that instantiate it with a specific XSLT stylesheet.
- Likewise, the graph provider derives the spanning tree of a graph to feed it to the Treebolic, it gets its data in turn from a xml document specified as either GXL, GXML...
Engine-Provider interface
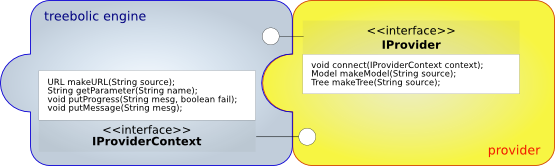
<<interface>>
IProvider
public void connect(IProviderContext context);
public Model makeModel(String source);
public Tree makeTree(String source);
- The connect() method is called by the framework (widget) to let itself be known to the provider as a provider context. The provider can then call back the the provider context to make a URL, get a parameter, and put some feedback information. The connect() method is guaranteed to be called first thing after contructing the provider class and before the invocation of makeModel or makeTree()
- The makeModel() method is called by the framework (widget) within the init() stage to retrieve tree data and settings (paired in a model).
- The makeTree() method is called by the framework (widget) at a later stage to retrieve extra tree data (excluding settings, which are unchanged). This happens when an extra branch is mounted/grafted on the existing tree, which retains its global settings.
<<interface>>
IProviderContext
public URL makeURL(String source);
public String getParameter(String name);
public void putProgress(String message, boolean fail);
public void putMessage(String message);
- This is how the framework is known to the provider.
- The getParameter() method is called to get either general-purpose or parameters that only the provider can make sense of.
- The putProgress() or putMessage() methods are used to provide visual feedback while data is loading or display an error message.
Context-Engine interface

<<interface>>
IContext
public URL getBase();
public URL getImagesBase();
public URL getHtmlDocumentBase();
public String getParameter(String name);
public Image getImage(URL url);
public boolean linkTo(String href, String target);
public void showStatus(String string);
- This is how the application is known to the framework (widget).
- The getBase() method is called by the framework to get the URL for the document container. This gives the application a chance to affect document search.
- The getImagesBase() method is called to get the URL of a folder (directory) that image files are to be loaded from.
- The linkTo() method gives the application a chance to process a link request (it returns true when it does so) or leave the framework handle it (it then returns false).
class
Widget
public void init();
public void init(String provider, String source);
public void reinit(String source);
public void init(Model model);
public void link(String url, String target)
public String match(String target, String scope, String mode);
public void focus(String nodeid);
- The application must call one of the init() methods.
- The init() method lets the framework determine the provider class and data.
- The init(provider, source) method specifies both the provider class and data source.
- The init(model) method bypasses the use of a provider. The model (data and settings) is directly delivered to the framework. This is used by the generator for example.
- The match() method is used by scripting languages to find a node matching specified search criteria. It returns the node ID if a node is found.
- The focus() method is used by scripting languages for a node (whose ID is passed as parameter) to receive focus.
- The link() method is used by scripting languages to force the framework to handle a URL request.
See interfaces as SVG






